How Heat Pumps Work?
If you’re in the market for a new heating and cooling system, you may be wondering if a heat pump is the right choice for your home. Heat pumps are becoming more and more popular, but many people still don’t know how they work. In this post, we’ll explain how heat pumps work and discuss the benefits of using one in your home.
What Is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is a type of HVAC system that is used to heat and cool a home. Unlike a furnace, which uses combustion to generate heat, a heat pump moves heat from one place to another. In the winter, a heat pump extracts heat from the air outside and brings it into your home. In the summer, the process is reversed and the heat pump moves heat from your home to the outdoors.
What Are the Different Types of Heat Pums ?
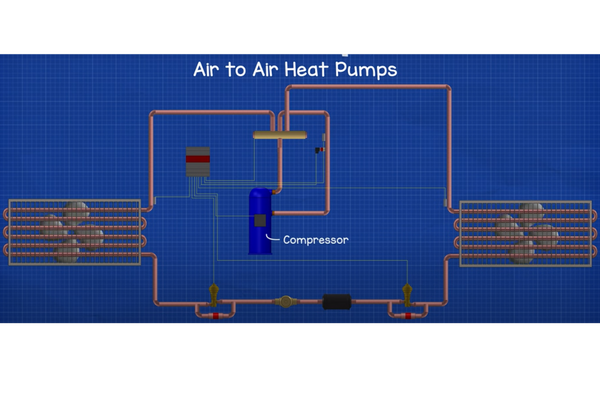
-Air-source: Air-source heat pumps are the most common type of heat pump. They use the air outside to generate heating and cooling power.
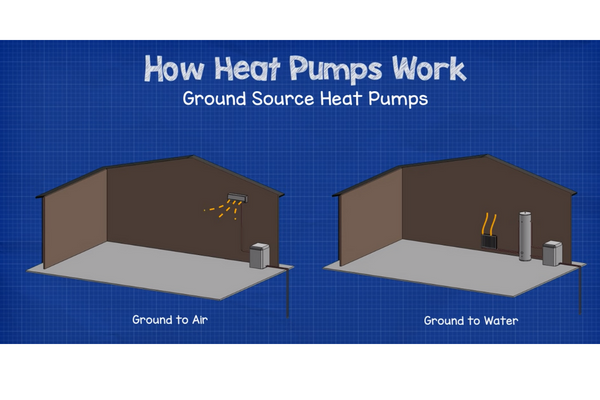
-Geothermal: Geothermal heat pumps use the ground or water to generate heating and cooling power. They are more efficient than air-source heat pumps, but they are also more expensive to install.
-Ground-source: Ground-source heat pumps are similar to geothermal heat pumps, but they use the ground instead of water to generate heating and cooling power.
How does Heat Pumps Work?
Heat Pump Basic Operation
The basic operation of a heat pump is simple. In the winter, the heat pump extracts heat from the air outside and brings it into your home. In the summer, the process is reversed and the heat pump moves heat from your home to the outdoors.
To understand how a heat pump works, it helps to know a little bit about the science of heat. Heat is a type of energy that flows from objects with higher temperatures to objects with lower temperatures. When the temperature difference between two objects is large, the flow of heat is high. When the temperature difference is small, the flow of heat is low.
The rate at which heat flows from one object to another is determined by three factors:
-The difference in temperature between the two objects
-The surface area of the objects
-The material that is separating the two objects
In order to maximize the flow of heat, you want to have a large temperature difference and a small separation. This is why a furnace is so effective at heating a home. The furnace generates heat at a very high temperature and then uses a blower to push the hot air into your home. The result is a large flow of heat from the furnace to your home.
A heat pump also generates a flow of heat, but it does so in a different way. Instead of using combustion to generate heat, a heat pump moves heat from one place to another. In the winter, a heat pump extracts heat from the air outside and brings it into your home. In the summer, the process is reversed and the heat pump moves heat from your home to the outdoors.
The efficiency of a heat pump is determined by its coefficient of performance (COP). The COP is a measure of how much heat the heat pump can generate for every unit of energy it uses. A COP of 1 means that the heat pump is 100% efficient. A COP of 2 means that the heat pump is 200% efficient. In other words, for every unit of energy the heat pump uses, it generates two units of heat.
The efficiency of a heat pump is affected by the temperature difference between the heat pump and the object it is trying to heat or cool. When the temperature difference is large, the heat pump has to work harder and its efficiency decreases. When the temperature difference is small, the heat pump can operate more efficiently.
This is why heat pumps are most efficient in moderate climates. In a climate with very cold winters and very hot summers, the heat pump will have to work harder to heat and cool your home, and its efficiency will decrease. In a climate with mild winters and cool summers, the heat pump can operate more efficiently.
Where Do Heat Pumps Work Best?

Heat pumps work best in moderate climates with mild winters and cool summers. In a climate with very cold winters and very hot summers, the heat pump will have to work harder to heat and cool your home, and its efficiency will decrease.
Important Components Of A Heat Pump System
-Outdoor Unit: The outdoor unit of a heat pump system contains the compressor and the condenser. The compressor pumps refrigerant through the system. The condenser releases heat from the refrigerant and dissipates it into the air.
-Indoor Unit: The indoor unit of a heat pump system contains the evaporator and the air handler. The evaporator absorbs heat from the air inside your home. The air handler blows air over the evaporator and into your home.
-Refrigerant: Refrigerant is a fluid that is used to transfer heat. It flows through the system and picks up heat from the indoor unit and delivers it to the outdoor unit.
-Reversing valve: The reversing valve is a valve that reverses the flow of refrigerant. In the cooling mode, the reversing valve directs refrigerant to the evaporator. In the heating mode, the reversing valve directs refrigerant to the condenser.
-Expansion valve: The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
Heat Transfer and Air-source Heat Pumps?

Heat pumps transfer heat by moving it from one place to another. In air-source heat pumps, the heat is transferred between the air outside and the air inside your home.
Ground-Source and Absorption Heat Pumps?
Ground-source heat pumps transfer heat between the ground and your home. Absorption heat pumps transfer heat between water and your home.
How do Heat Pumps Work in the Summer?
In the summer, a heat pump transfers heat from your home to the outdoors. The outdoor unit contains the compressor and the condenser. The compressor pumps refrigerant through the system. The condenser releases heat from the refrigerant and dissipates it into the air.
The indoor unit contains the evaporator and the air handler. The evaporator absorbs heat from the air inside your home. The air handler blows air over the evaporator and into your home.
The reversing valve directs refrigerant to the evaporator. The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
How do Heat Pumps Work in the Winter?
In the winter, a heat pump transfers heat from the outdoors to your home. The outdoor unit contains the compressor and the condenser. The compressor pumps refrigerant through the system. The condenser releases heat from the refrigerant and dissipates it into the air.
The indoor unit contains the evaporator and the air handler. The evaporator absorbs heat from the air inside your home. The air handler blows air over the evaporator and into your home.
Pros and Cons of Heat Pumps

When it comes to home heating and cooling, there are a lot of options out there. One option that has been gaining popularity in recent years is the heat pump. Heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling, and they are generally more energy-efficient than other options.
However, heat pumps are not without their drawbacks. Here are some pros and cons of heat pumps to consider before making a decision for your home.
Pros of Heat Pumps
1. Energy-Efficient
Heat pumps are one of the most energy-efficient options for heating and cooling your home. They use a small amount of electricity to move heat from one place to another, which is much more efficient than other methods of heating and cooling.
2. Can Be Used in All Climates
Heat pumps can be used in all climates, although they are most commonly used in milder climates. In colder climates, they can be used in conjunction with a backup heating system, such as a furnace.
3. Low Maintenance
Heat pumps require very little maintenance and are typically very reliable.
4. Versatile
Heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling, making them a versatile option for your home.
5. Long lifespan
Heat pumps typically have a long lifespan, lasting for many years with proper maintenance.
Cons of Heat Pumps
1. Initial Cost
The initial cost of a heat pump can be higher than other heating and cooling options. However, the long lifespan and energy-efficiency of heat pumps can offset the initial cost over time.
2. Not Ideal for Extreme Climates
Heat pumps are not ideal for extreme climates, both hot and cold. In very cold climates, a backup heating system is typically necessary. In very hot climates, heat pumps can struggle to keep your home cool.
3. Requires Regular Maintenance
Heat pumps require regular maintenance, such as yearly tune-ups, in order to keep them running properly.
4. Can Be Noisy
Heat pumps can be noisy, especially the outdoor units. If noise is a concern, you may want to look into a different heating and cooling option.
5. Limited Warranty
Heat pumps typically come with a limited warranty, so be sure to read the fine print before making your purchase.
What to Look for in a Heat Pump?

When shopping for a heat pump, there are a few things you should keep in mind. First, think about the climate you live in and whether or not a heat pump would be a good fit. If you live in an extreme climate, a heat pump may not be the best option.
Next, consider the size of your home. Heat pumps are available in a variety of sizes, so you’ll want to make sure you get one that is big enough to heat or cool your entire home.
Finally, think about your budget. Heat pumps can be a big investment, so be sure to shop around and compare prices before making your final decision.
Heat pumps are a popular choice for home heating and cooling, but they are not right for everyone. Be sure to consider the pros and cons of heat pumps before making a decision for your home. With a little research, you can find the perfect heating and cooling solution for your needs.
Do Heat Pumps Save You Money?

Heat pumps are often advertised as a way to save money on your heating and cooling bills. But do they actually live up to the hype?
The answer is yes and no. Heat pumps can save you money on your energy bills, but only if they are used correctly. In some cases, heat pumps can actually end up costing you more money.
Here are a few tips to help you save money with your heat pump:
1. Use the thermostat wisely. One of the biggest mistakes people make with their heat pump is using the thermostat incorrectly. If you set the thermostat too low in the winter, your heat pump will have to work overtime to maintain the temperature, which will end up costing you more money. Likewise, if you set the thermostat too high in the summer, your heat pump will struggle to keep your home cool, leading to higher energy bills.
2. Invest in regular maintenance. Heat pumps require regular maintenance, such as tune-ups and filter changes, in order to run properly. By investing in regular maintenance, you can keep your heat pump running efficiently and avoid costly repairs down the road.
3. Consider a zoning system. If you have a large home, consider installing a zoning system. Zoning systems allow you to control the temperature in different areas of your home, so you’re not wasting energy heating or cooling rooms that you’re not using.
4. Upgrade to a more efficient model. If your heat pump is more than 10 years old, it may be time to upgrade to a more efficient model. Newer models are much more energy-efficient, so they can save you money on your energy bills.
5. Add insulation. Another way to save money with your heat pump is to add insulation to your home. By insulating your walls and attic, you can keep the heat in your home longer, which will reduce the amount of work your heat pump has to do.
By following these tips, you can save money on your energy bills and keep your heat pump running efficiently. Heat pumps are a great way to save money, but only if you use them correctly. With a little bit of effort, you can keep your energy costs down and enjoy the comfort of your home.
Heat Pump Maintenance

Heat pumps require regular maintenance in order to run properly. Here are a few tips to keep your heat pump running efficiently:
1. Schedule regular tune-ups. Heat pumps should be tuned up at least once a year. During a tune-up, a technician will clean the unit and check for any potential problems. This can help prevent expensive repairs down the road.
2. Change the filters regularly. Heat pump filters should be changed every three months or so. Dirty filters can cause your heat pump to work harder than it needs to, leading to higher energy bills.
3. Keep the area around your heat pump clean. The area around your heat pump should be free of debris, such as leaves and twigs. This can help prevent your heat pump from overworking itself.
4. Check for leaks. Heat pumps can develop leaks over time. These leaks can let cool air escape, making your heat pump work harder than it needs to. If you notice a leak, be sure to have it repaired as soon as possible.
5. Upgrade to a more efficient model. If your heat pump is more than 10 years old, it may be time to upgrade to a newer, more energy-efficient model. Newer models are much more efficient, so they can save you money on your energy bills.
FAQs
1. How often should I have my heat pump serviced?
Heat pumps should be serviced at least once a year. During a service, a technician will clean the unit and check for any potential problems. This can help prevent expensive repairs down the road.
2. What are some signs that my heat pump needs to be replaced?
If your heat pump is more than 10 years old, it may be time to replace it. Additionally, if your heat pump is leaking coolant or if it’s not heating or cooling your home properly, it may need to be replaced.
3. How can I improve the efficiency of my heat pump?
There are a few things you can do to improve the efficiency of your heat pump. First, make sure that the area around your heat pump is free of debris. Additionally, you can add insulation to your home or install a zoning system. These things can help your heat pump run more efficiently.
4. What are some common problems with heat pumps?
Heat pumps can develop a number of problems over time. Common problems include leaks, dirty filters, and clogged coils. If you notice any of these problems, be sure to have your heat pump serviced as soon as possible.
5. How much does it cost to repair a heat pump?
The cost of repairing a heat pump will vary depending on the problem. However, most repairs will fall somewhere between $100 and $500. Additionally, you may need to replace your heat pump if it’s more than 10 years old.
6. How much does it cost to replace a heat pump?
The cost of replacing a heat pump will vary depending on the size and type of heat pump you need. However, most heat pumps will cost between $2,000 and $5,000. Additionally, you may need to pay for installation, which can cost between $500 and $1,500.
7. What are some tips for maintaining my heat pump?
There are a few things you can do to maintain your heat pump. First, make sure to have it serviced at least once a year. Additionally, you should change the filters every three months and keep the area around your heat pump clean. Lastly, you should check for leaks and have them repaired as soon as possible.
8.What is the major problem of heat pump?
One major problem that can occur with heat pumps is that they can develop leaks. These leaks can let cool air escape, making your heat pump work harder than it needs to. If you notice a leak, be sure to have it repaired as soon as possible.
9.Do heat pumps need to be on all the time?
No, heat pumps do not need to be on all the time. In fact, it’s best to turn them off when you’re not using them. This can help save you money on your energy bills.
10.What is the downside to a heat pump?
One downside to heat pumps is that they can be expensive to repair. Additionally, if your heat pump is more than 10 years old, it may need to be replaced.
11.How long should a heat pump run per day?
Heat pumps should run for about 30 minutes per day. However, this may vary depending on the climate you live in.
12.How do I know if my heat pump is working properly?
One way to tell if your heat pump is working properly is to listen for strange noises. Additionally, you can check to see if your heat pump is blowing hot or cold air. Lastly, you can check your energy bills to see if they’ve increased. If you notice any of these things, be sure to have your heat pump serviced.
13.At what temp do heat pumps stop working?
Heat pumps typically stop working when the temperature outside is below freezing. However, some heat pumps are designed to work in colder climates.
14.How do I thaw a frozen heat pump?
If your heat pump is frozen, you can try thawing it with a hairdryer. Additionally, you can turn off your heat pump and let it thaw on its own. However, if your heat pump is severely frozen, you may need to call a professional.
15.Why has my heat pump stopped working?
There are a few reasons why your heat pump may have stopped working. First, the area around your heat pump may be too cold. Additionally, your heat pump may be leaking coolant. Lastly, your heat pump may be dirty or clogged. If you notice any of these problems, be sure to have your heat pump serviced as soon as possible.
15.Do heat pumps use a lot of electricity?
No, heat pumps do not use a lot of electricity. In fact, they are one of the most efficient heating and cooling systems available. However, heat pumps can be expensive to operate in very cold climates.
Conclusion
A heat pump is an appliance that helps to keep your home comfortable by transferring heat from one place to another. It does this by using a refrigerant to absorb heat from the surrounding air and then releasing it into the indoor space. Heat pumps come in both air-source and ground-source varieties, and can be used either to cool or heat your home. If you’re considering purchasing a heat pump for your home, it’s important to understand how they work so you can choose the right type for your needs. Now that you know all about how these appliances operate, are you ready to buy one?
>> Best Heat Pumps Consumer Reports
See more :
- How To Sharpen Kitchen Knives?
- How Heat Pumps Work?
- How To Install Gutter Guards?
- How to Vacuum A Pool?
- How To Paint Kitchen Cabinets?
- How Do Air Fryers Work?
- How Do Metal Detectors Work?
Reference source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_pump
I’m Georgie Barton, a reviewer for various magazines and consumer reports. I’ve been testing and writing about household products and electronics for years, and have become quite the authority on the subject. My goal is to help people make informed decisions when purchasing these items, so they can get the most value for their money.
My hope is that through my work, everyone will be able to find a quality and satisfactory product. Thank you for reading!
